Research
How do our psychological mechanisms perform in and adapt to our hyper-socialized, hyper-accelerated modern world of social media, smartphones, and cultural digitization?
Social media platforms, digital culture companies, and government agencies are all worried about the role that online cultural conflict, political polarization, bias, and mental health play in trust, safety, society, and AI alignment.
I study the psychological and cultural mechanisms that underlie these issues of digital cultural conflict; attention bias to threat, intergroup dynamics, cross-cultural morality, intersectional prejudice, and hate-based rhetoric online.
Given my background in international conflicts and their interplay with technology and culture, my work explores how to leverage experimental data, anthropological research, and computational methods to measure, analyze, and combat threat and conflict both online and in the real world.


AI Ethics, Alignment, & SocioTechnical Systems
Against GPTology : A cautionary approach to LLMs in Psychology
Carelessly using LLMs in psychological studies, a trend we rhetorically refer to as ``GPTology,'' can have negative consequences, especially given the convenient access to models such as ChatGPT.
We elucidate the promises, limitations, and ethical considerations of using LLMs in psychological research including the substantial psychological diversity around the globe and within populations, narrowing down psychology's methodological toolbox with LLM annotation, and the need to develop both methods and standards to compensate for LLMs' opaque black-box nature to facilitate reproducibility, transparency, and robust inferences from AI generated data.

The Shrinking Landscape of Linguistic Diversity in the Age of Large Language Models
“We’re getting the language into its final shape– the shape it’s going to
have when nobody speaks anything else.” George Orwell, 1984
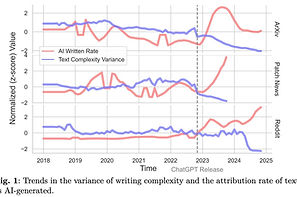
How do LLMs shape the way we write? Our research shows that LLM-assisted writing is making language more uniform, reducing linguistic diversity, and altering how personal traits are expressed through text. These shifts have profound implications for identity, culture, and fairness.
We analyzed writing across multiple platforms and found a measurable decline in the variance of linguistic complexity after ChatGPT’s introduction. Controlled experiments confirmed that LLMs consistently homogenize writing styles, reinforcing this trend at scale. But the impact goes beyond style. LLMs also weaken the connection between language and personal traits, subtly shifting how authors are perceived. This challenges long-established linguistic markers used in areas like personality assessment and demographic inference.
These findings raise critical questions: How does AI-assisted writing influence hiring, education, and cultural expression? As LLMs standardize language, they may also shape social and professional opportunities in ways we don’t yet fully understand.
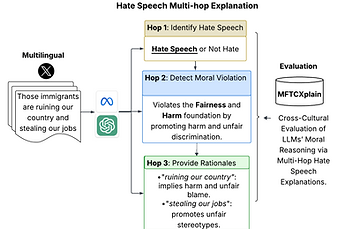
MFTCXplain: A Multilingual Benchmark Dataset for Evaluating the Moral Reasoning of LLMs through Hate Speech Multi-Hop Explanations
Can interpretable methods reveal cross‑cultural patterns in how LLMs understand the moral reasoning behind hate speech?
We’re excited to introduce "MFTCXplain, the first multilingual benchmark dataset for evaluating the moral reasoning of LLMs through multi‑hop hate speech explanation". It consists of 3,000 hate speech tweets annotated with Moral Foundations Theory (MFT) labels, along with text‑span rationales, across four languages: Portuguese, Persian, Italian, and English. Moreover, we introduce a new interpretable approach for assessing hate speech detection and the moral reasoning behind it.
Empirical results on MFTCXplain reveal that hate speech rarely occurs without the presence of moral sentiments. They also show a consistent misalignment between LLM outputs and human rationales, highlighting the limited capacity of current LLMs to internalize and reflect human moral reasoning.
How to Teach Humans to Teach AI to Analyze
Police Footage: A Human-Centered Framework for
Responsible Subjective AI in Sociotechnical
Systems
Deploying AI to analyze police body-worn camera footage raises technical, ethical, and sociocultural challenges: the data are multimodal and egocentric; interpretations are contested; and “ground truth” depends on perspective. At the crux of all of these are the humans who build and use this meaningful AI.
We present a human-centered annotation framework for building multimodal, multi-perspective AI to analyze LAPD traffic-stop footage, centering the human side of human-centered AI. Our approach integrates stakeholder engagement across communities, government, and industry; recruitment and training of a demographically and experientially diverse annotator pool; iterative guideline and software development; and adaptations to logistical and budget constraints. We prioritize preserving perspectival diversity while mitigating bias, protecting annotator well-being, and ensuring governance suited for high-stakes use.
Disagreement is treated as signal, not noise, with labels designed for soft-target modeling. We share lessons for adapting this blueprint to other contested domains. Without such intentional design, subjective AI risks erasing marginalized perspectives, undermining trust, and harming the very humans it is meant to protect and benefit.


Experimental Studies of Conflict on Social Media
Ideological Threat on Twitter Influences Political Prejudice
How do ideologically relevant threats influence people from different political ideologies?
In three experimental studies (N=1600) we show that ideologically relevant threats (on Twitter and in real-life) influence outgroup prejudice. Exploratory time-series analyses (N=34,000) shows how ideologically threatening events influence partisan polling data. Our studies support the notion that Progressives and Conservatives are threatened by different topics and show experimentally that exposure increases the endorsement of prejudice.

Targeting audiences’ moral values shapes misinformation sharing on Facebook and Twitter
Does targeting audiences’ core values facilitate the spread of misinformation?
We analyze real-world Twitter data (N = 20,235; 809,414 tweets) on COVID vaccine misinformation, in conjunction with a set of behavioral experiments (N=1600) and find that aligning the moral framing with individuals' moral values increases the spread of misinformation. Framing posts to match people's moral values led to higher sharing intentions, regardless of the accuracy of the content, suggesting that targeting core values can influence the dissemination of information on social media.

Fighting Fire with Fire: How groups incentivize incivility on Reddit
Groups usually punish group members that violate norms of civility (i.e., rudeness or vulgarity). However, online (i.e., social media) discourse often derails into tit-for-tat cycles of incivility.
Analysis of Reddit data (N = +100k; +1M posts) and follow up experimental studies found that incivility is driven by groups rewarding members for defending the group from perceived outgroup attacks, thus incentivizing incivility to “fight fire with fire".

Politics in Social Media Bios Influence Polarization
What is the impact of including political identity markers in your social media bio?
This project aims to address three key questions: (1) What kinds of direct and indirect political identity signals are in social media bios? (2) How prevalent are these political bios? and (3) What are the attitudes of individuals across the political spectrum towards those who display political bios? This project explores the dynamic influence of politics within social media bios on political prejudice and polarization.

Morality Across Culture, Time, and Technology
County-level Moral Values Predict Covid 19 Vaccination Rates
Why are Americans hesitant to get their Covid-19 vaccinations?
Our research shows that the moral value of purity can predict vaccine hesitancy at the US county level beyond religiosity and political orientation.

The Moralization of Wealth Across Cultures -
Is Elon Musk Disgusting?
Why do some people morally justify excessive wealth in a world where so many struggle?
We examine how people's moral values and national inequality predict the moralization of excessive wealth across 20 nations (N = 4,351), and find notable variability such that more equal societies (e.g., Belgium, Switzerland) consider having too much money more wrong. People's purity concerns predict their moralization of excessive wealth across societies, especially in economically egalitarian nations, after controlling for other moral intuitions, moralization of inequality, religiosity, political ideology, and demographic variables.

The Moral Language of Hate
Is there a certain moral rhetorical pattern to hate and violence?
In three studies, our research found a moral tone of purity and spiritual degradation underlying the hateful language in Nazi Propaganda, hateful slurs as they occur in multitude of languages, and hate speech on social media platforms.

Moral Congressional Speeches Predict a Polarized Congress
Can the moral language of congressional speeches inform us of polarization?
Our study shows that partisan roll-call votes in congress can be predicted by moral rhetoric, divisive language .

Investigating Morality, Hate, and Bias in Digital Culture
The Moral Foundations Reddit Corpus
How do people speak about morality online and how does it relate to offline behavior? How does the moral language on Reddit differ from other social media platforms? How do we teach machine learning algorithms about how people speak about moral values?
Our project aims to answer these questions by providing the Moral Foundations Reddit Corpus, a collection of 16, 123 Reddit comments that have been curated from 12 distinct subreddits, hand-annotated by at least three trained annotators for 8 categories of moral sentiment.

Hateful Rhetoric in the Civil Comments News Corpus
What type of hate do we find in the comments of online news stories?
In collaboration with Google Jigsaw, we examined the types of hate-based rhetoric expressed in uncivil comments on online news. We hand annotated 16,099 comments from the toxic spans dataset for our sociological, psychological, and legal theory influenced construct of hate based rhetoric. This includes assaults on human dignity, calls to violence, vulgarity, the targeted group of hate, and whether the hate was expressed implicitly or explicitly.

LAPD Bodyworn Police Camera Footage Project
Policing is problematic, politicized, and now recorded. How do we better understand officer civilian communication by analyzing the footage of LAPD’s 8k active body worn cameras?
In collaboration with NSF, Microsoft, and LAPD, our ongoing project proposes a large-scale (30k videos), city-wide analysis of body-worn camera footage using state-of the-art explainable machine learning techniques and diverse stakeholder perspectives on what good communication looks like. This will facilitate increased transparency and accountability of police, enable data-driven, community-informed policy advocacy, and provide powerful new machine learning tools for use nationally.


Occasionally, researchers leave the lab and complete triathlons. (right: Dr. Nina Christie USC)
